Step-by-step explanation
Differentiating both sides of the equation with respect to x:
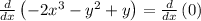
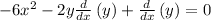
Isolating d(y)/dx:
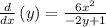
Differentiate again both sides of the equation with respect to x:
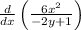
Take the constant out:
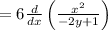
Applying the quotient rule:
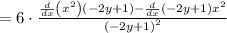
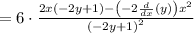
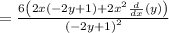
The expression now is as follows:
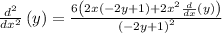
Substituting d(y)/dx= 6x^2/(-2y+1):
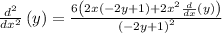
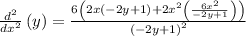
Simplifying the expression by removing the parentheses:
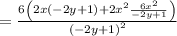
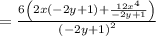
Convert the element to a fraction:
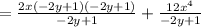
Since the denominators are equal, combine the fractions:
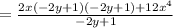
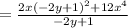
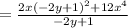
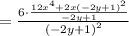
Simplifying:
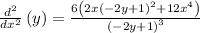
The final implicit derivative is as follows:
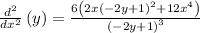
Now, we need to find the implicit derivative at point (-1,2):
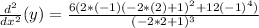
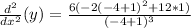
Adding numbers:
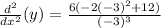
Computing the powers:
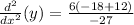
Adding numbers:
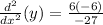
Multiplying numbers:
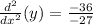
Simplifying:
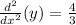
The value of the Implicit Derivative at the point (-1,2) is 4/3