Answer:
option (b) is correct.
First step to solve for deriving the quadratic formula from the quadratic equation is completing the square.
Explanation:
Given : the quadratic equation
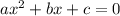
We have to find the first step for deriving the quadratic formula from the quadratic equation.
Quadratic formula is given by

Consider the given quadratic equation
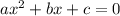
Divide the equation by a, we get,

Take
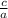 to other side, we get,
to other side, we get,

Add
 to both side, we get,
to both side, we get,

Thus, the left side is in the form of
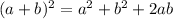
On solving, we get,

Then solve for x , we get quadratic formula

Thus, first step to solve for deriving the quadratic formula from the quadratic equation is completing the square.
Thus, option (b) is correct.