Answer : The new pressure of gas will be, 25.176 kPa
Solution :
Gay-Lussac's Law : It is defined as the pressure of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas at constant volume and number of moles.

or,

where,
 = initial pressure of gas = 29.4 kPa
= initial pressure of gas = 29.4 kPa
 = final pressure of gas = ?
= final pressure of gas = ?
 = initial temperature of gas =
= initial temperature of gas =

 = final temperature of gas =
= final temperature of gas =
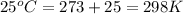
Now put all the given values in the above equation, we get the final pressure of gas.


Therefore, the new pressure of gas will be, 25.176 kPa