Answer:
The velocity after the collision is 2.82 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Law Of Conservation Of Linear Momentum
It states the total momentum of a system of bodies is conserved unless an external force is applied to it. The formula for the momentum of a body with mass m and speed v is
P=mv.
If we have a system of two bodies, then the total momentum is the sum of the individual momentums:
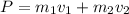
If a collision occurs and the velocities change to v', the final momentum is:
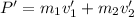
Since the total momentum is conserved, then:
P = P'
Or, equivalently:
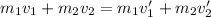
If both masses stick together after the collision at a common speed v', then:
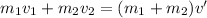
The common velocity after this situation is:
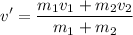
There is an m1=3.91 kg car moving at v1=5.7 m/s that collides with an m2=4 kg cart that was at rest v2=0.
After the collision, both cars stick together. Let's compute the common speed after that:
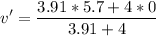
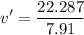
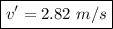
The velocity after the collision is 2.82 m/s