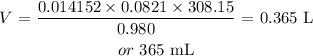Answer:
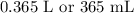
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to get the volume in liters occupied by the gas
From the ideal gas law:
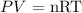
This means:
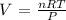
where:
n is the number of moles. To get this, we have to divide the mass given by the molar mass of the gas
The number of moles is as follows:
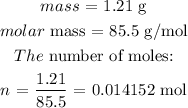
R is the molar gas constant which is 0.0821 L.atm/mol.k
T is the temperature in Kelvin. We calculate this by adding 273.15 K to the temperature in Celsius (273.15 + 35 = 308.15 K)
P is the pressure of the gas which is 0.980 atm
V is the volume that we want to calculate
Substituting the values, we have it that: