Answer: Thus the standard potential for an electrochemical cell with the cell reaction that follows is 0.84 V.
Step-by-step explanation:
Standard potential for an electrochemical cell is given by:
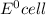 = standard electrode potential =
= standard electrode potential =
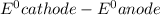
The
 values have to be reduction potentials.
values have to be reduction potentials.
Given: Reduction potential for atom X:

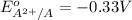
The element A with negative reduction potential will lose electrons undergo oxidation and thus act as anode.The element X with positive reduction potential will gain electrons undergo reduction and thus acts as cathode.
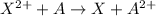
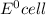 = standard electrode potential =
= standard electrode potential =
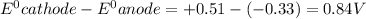
Thus the standard potential for an electrochemical cell with the cell reaction that follows is 0.84 V.