The correct answer to the question will be that the electric force between them will be decreased.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let us consider the charge contained by A and B are denoted as Q and Q' respectively.
Let R is the separation distance between them.
As per Coulomb's law in electrostatics, the force of attraction or repulsion between the two charge bodies A and B will be -
Coulombic force F =
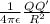
Here,
 is the permittivity of the medium in which the charges are present.
is the permittivity of the medium in which the charges are present.
From above, we see that electric force is inversely proportional to the square of separation distance between them.
Mathematically it can be written:
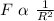
As per the question, the distance between A and B is increased.
Hence, the electric force between A and B will be decreased.