the first expression :
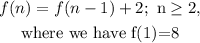
so at n=2,
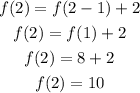
put n=2 in the equation f(n) = 2n +6
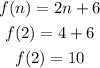
so,
f(n)=f(n-1)+2 is equal to f(n) =2n +6
Now for expression 2 :
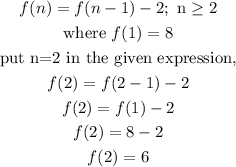
put n=2 in the expression f(n)=-2n+10
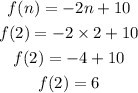
In both the expression at n=2, f(2)=6 so,
f(n)=f(n-1)-2 is equal to f(n)=-2n+10.
Now expression 3:
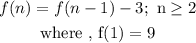
put n=2,
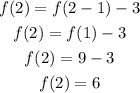
Now for the expression at the entry of third coloumn,
f(n)=-3n+12
put n=2
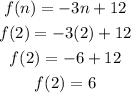
since, the f(2) =6,