Answer:
If the volume of a gas increased from 2 to 6 L while the temperature was held constant, the pressure of the gas decreased by a factor of 3.
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's law that says "The volume occupied by a given gaseous mass at constant temperature is inversely proportional to pressure." This means that if the pressure increases, the volume decreases, while if the pressure decreases, the volume increases.
Boyle's law is expressed mathematically as:
Pressure * Volume = constant
or
P * V = k
To obtain the proportionality factor k you must make the quotient:
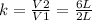
k= 3
This means that if the volume of a gas increased from 2 to 6 L while the temperature was held constant, the pressure of the gas decreased by a factor of 3.