Let's start by balancing the reaction:
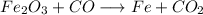
As we can see, C appears only on two comopunds, CO and CO₂, and since both have 1 C each, their coefficients have to be the same for C to be balanced. However, CO has 1 O and CO₂ has 2, so there is a difference of 1 O betwee them.
The other source of O is Fe₂O₃, that has 3 O. So, we must choose a coefficient for CO and CO₂ such that the difference between the numbers of O is a multiple of 3, that way we can fix this difference with the O from Fe₂O₃. So, we can put coefficients of 3 on both of them:
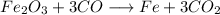
That way, we maintained C balanced (3 on each side) and now we have 3 + 3 O on the left side and 6 O on the right side, so the same amount.
Now, we just have to calance Fe, but it is easy since we have it alone in Fe. Since we have 2 on the left side, it is enough to put a coefficient of 2 on Fe to get the balanced reaction:

Now, to convert from mass to number of moles, we need the molar masses of the reactants, which we can calculate from the atomic weights of the elemnts in each of them:
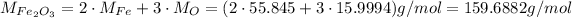
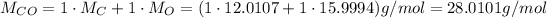
Now, we can convert their masses to number of moles:
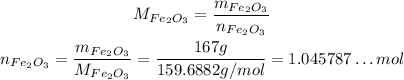
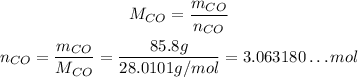
Now, to determine the limiting reactant, we need to divide both the number of mole by their coefficients on the balanced reaction, so we can see how many we need per reaction of each:
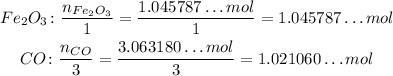
Now, the limiting reactant is the one we have less number of moles per reaction. We can see that we have less CO than Fe₂O₃, so the limiting reactant is CO.