Answer:
The explosive force experienced by the shell inside the barrel is 23437500 newtons.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let suppose that shells are not experiencing any effect from non-conservative forces (i.e. friction, air viscosity) and changes in gravitational potential energy are negligible. The explosive force experienced by the shell inside the barrel can be estimated by Work-Energy Theorem, represented by the following formula:
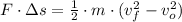 (1)
(1)
Where:
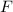 - Explosive force, measured in newtons.
- Explosive force, measured in newtons.
 - Barrel length, measured in meters.
- Barrel length, measured in meters.
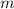 - Mass of the shell, measured in kilograms.
- Mass of the shell, measured in kilograms.
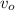 ,
,
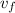 - Initial and final speeds of the shell, measured in meters per second.
- Initial and final speeds of the shell, measured in meters per second.
If we know that
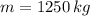 ,
,
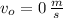 ,
,
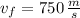 and
and
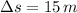 , then the explosive force experienced by the shell inside the barrel is:
, then the explosive force experienced by the shell inside the barrel is:
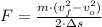
![F = ((1250\,kg)\cdot \left[\left(750\,(m)/(s) \right)^(2)-\left(0\,(m)/(s) \right)^(2)\right])/(2\cdot (15\,m))](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/nzjx5jfbhfswm6phkb3ve2dc2za4otuavl.png)
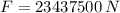
The explosive force experienced by the shell inside the barrel is 23437500 newtons.