Answer
The specific heat of the substance is 2.15 J/g⁰C
Step-by-step explanation
Given:
Quantity of heat, Q = 386 J
Mass of the substance, m = 3.2 g
Initial temperature, T₁ = 23 ⁰C
Final temperature, T₂ = 79 ⁰C
What to find:
The specific heat of the substance.
Step-by-step solution:
The specific heat of the substance, c can be calculated using the formula below.
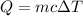
ΔT = T₂ - T₁ = 79 ⁰C - 23 ⁰C = 56 ⁰C
So plugging Q = 386 J, m = 3.2 g and ΔT = 56 ⁰C into the formula, we have
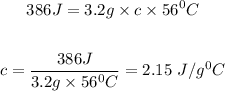
The specific heat of the substance is 2.15 J/g⁰C