The bond between which atoms is most likely responsible for giving the compound its high melting point is: c. oxygen (O) and carbon (C)
Ionic bonds, exemplified by the interaction between oxygen (O) and potassium (K), are renowned for their high melting points due to the formidable electrostatic forces they entail. In the case of potassium acetate (
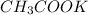 ), a compound with ionic characteristics, these robust forces stem from the attraction between positively charged potassium ions (K+) and negatively charged acetate ions (
), a compound with ionic characteristics, these robust forces stem from the attraction between positively charged potassium ions (K+) and negatively charged acetate ions (
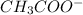 ). The formation of ionic bonds involves the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the creation of charged ions. The compelling forces of attraction between these ions necessitate a substantial input of energy to disrupt, contributing to the elevated melting point exhibited by ionic compounds like potassium acetate. This property underscores the resilience of the electrostatic interactions that characterize ionic bonding, emphasizing their role in determining the physical properties of substances in this chemical category.
). The formation of ionic bonds involves the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the creation of charged ions. The compelling forces of attraction between these ions necessitate a substantial input of energy to disrupt, contributing to the elevated melting point exhibited by ionic compounds like potassium acetate. This property underscores the resilience of the electrostatic interactions that characterize ionic bonding, emphasizing their role in determining the physical properties of substances in this chemical category.