Answer:
The parent function of a quadratic function is
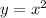
Now, if we add units we can move this function upwards, downwards leftwards and rightwards.
If we add a positive number to the x-variable, then the graph will move to the left.
If we add a negative number to the x-variable, then the graph will move to the right.
If we add a positive number to y-variable, then the graph will move upwards.
If we add a negative number to y-variable, then the graph will move downwards.
So, if we have the function
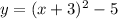
We would now that this functions is a parent function moved 3 units leftwards and 5 units downwards, that's how you deduct the translations.
Now, if we compare the rules we use before with linear function, there's no distinction between horizontal and vertical movements, because if we add to x-variable, then y-variable will be also affected.
For example, consider the parent function
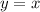
If we transform it to
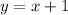 , then the whole line will move up 1 unit, or it will move to the left 1 unit, it's the same. The images attached show this.
, then the whole line will move up 1 unit, or it will move to the left 1 unit, it's the same. The images attached show this.
The second image attached show the transformation applied to the quadratic function. Notice the difference between the linear function and the quadratic function transformation.