Answer:This is because the KCl van'T Hoff factor is greater than the van'T Hoff factor of glucose in water.
Step-by-step explanation:
van't Hoff factor of KCl =
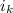 =2
=2
van't Hoff factor of glucose=
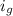 =1
=1
Elevation in boiling point is given by:
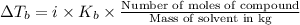
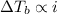
Mass of the water and
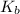 are same in both solution ,
are same in both solution ,
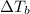 will depend upon van't Hoff factor of the compound.
will depend upon van't Hoff factor of the compound.
- Higher the Van't Hoff number more will be the elevation in boiling point of the solution.
- Lower the Van'T Hoff number lessor will be elevation is boiling point of the solution.
Since,
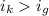 which means solution with KCl has more elevation is boiling point than the solution glucose.
which means solution with KCl has more elevation is boiling point than the solution glucose.