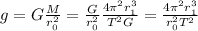Let's do it algebraically by first defining some variables. Use SI units.
Radius of the planet:
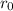
Distance between the spacecraft and the center of the planet:
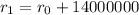
Mass of the planet:
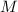
Mass of the spacecraft:
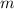
Tangential velocity of the spacecraft in its orbit:

Angular velocity of the spacecraft:
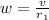
Orbital period of the spacecraft:
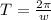
Since the centripetal force acting on the spacecraft is the gravitational force from the planet at distance
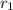
from the planet's centre:
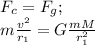
Note we can cancel out the mass of the spacecraft.
Using the formula in the definitions above, substitute:
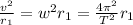
So we can substitute for this expression and obtain
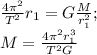
So now that we have the mass of the planet, we can easily calculate that
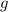
, the acceleration due to gravity on its surface, is given by: