Answer:
The specific heat of water would be 4.18 J/gK.
Step-by-step explanation:
You can realize that iron is losing heat and water is gaining heat. Based on the energy conservation law:
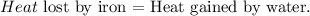
We want to find the specific heat of water 'c'. The formula of each heat - lost or gained- is:
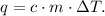
You can see that the change of temperature of iron is from 150 °C to 25 °C and the change of temperature of water is from 20 °C to 25 °C. Remember that the formula of ΔT is:
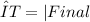
The change of temperature in celsius will be the same in kelvin. So our initial formula would be:
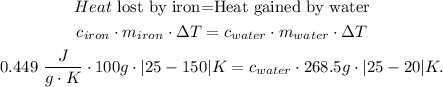
And finally, we solve for 'c' of water:
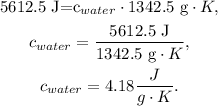
The specific heat of water would be 4.18 J/gK.