Answer:
C. There is a triple carbon-bond in the molecule.
Step-by-step explanation:
Under IUPAC nomenclature system, the hydrocarbons are termed on the basis of number of bonds present between carbon-carbon atoms joining together.
In case of aliphatic hydrocarbons;
The hydrocarbons with single C-C bonds are termed as alkane and all the compounds with such configuration are named with suffix -ane. For example- Methane(
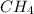 )
)
The hydrocarbons with double C=C bonds are termed as alkene and all the compounds with such configuration are named with suffix -ene. For example- Ethene (
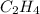 )
)
The hydrocarbons with triple C≡C bonds are termed as alkyne and all the compounds with such configuration are named with suffix -yne. For example- Ethyne (
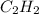 )
)
Hence, the hydrocarbon having suffix -yne in the name, indicates the presence of a triple bond between carbon-carbon atoms.