Answer:
The motorcyclist is 55 miles east of the small town.
Step-by-step explanation:
Motion With Constant Acceleration
It's a type of motion where the velocity of an object changes uniformly in time.
The equation that rules the change of velocities is:
![v_f=v_o+at\qquad\qquad [1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/zqckt89rlb2v0qgonskyi9dd240h8tlbek.png)
Where:
a = acceleration
vo = initial speed
vf = final speed
t = time
The distance traveled by the object is given by:
![\displaystyle x=v_o.t+(a.t^2)/(2)\qquad\qquad [2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/zh283gv9qnf95esv02n7ge67bq5asru6vj.png)
Using the equation [1] we can solve for a:
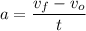
Solving [1] for t and substituting into [2] we get the following equation:
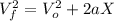
The motorcyclist has an acceleration of a=4\ m/s^2 and an initial distance of 5 m where he travels at vo=15 m/s. It's required to calculate the distance when the speed is vf=25 m/s.
Solving the last equation for X:
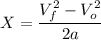
Substituting:
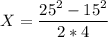
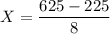
X = 50 m
Adding the initial distance:
The motorcyclist is 55 miles east of the small town.