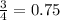Pre Image having vertices : △ABC with vertices A(−5, −4), B(−7, 3), C(3, −2)
Image having vertices : △A′B′C′ with vertices A′(−3.75, −3), B′(−5.25, 2.25), C′(2.25, −1.5).
As, Size of Preimage > Size of image
So, 0<Dilation Factor <1
When a triangle is dilated , the preimage and image are similar to each other .
Scale factor can be get through by finding the ratio of any of corresponding sides of triangle.
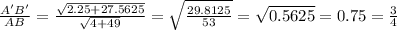
So, Scale Factor of Dilation =