Final answer:
The stationary weight of the astronaut at a position 4230 kilometers above Earth's surface is approximately 680.5 Newtons.
Step-by-step explanation:
First, we need to calculate the distance, r, from the center of the Earth to the position 4230 kilometers above Earth's surface. The radius of the Earth, R, is given as 6380 km. So, r = R + 4230 km = 6380 km + 4230 km = 10610 km.
Next, we can use Newton's law of universal gravitation to find the gravitational force, F, on the astronaut. The formula is F = (G * m1 * m2) /
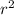 , where G is the gravitational constant, m1 is the mass of the astronaut, and m2 is the mass of the Earth. Plugging in the values, we get F =
, where G is the gravitational constant, m1 is the mass of the astronaut, and m2 is the mass of the Earth. Plugging in the values, we get F =
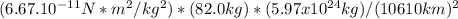 . Simplifying this calculation gives approximately 680.5 Newtons.
. Simplifying this calculation gives approximately 680.5 Newtons.