Answer:
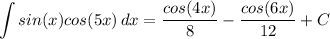
General Formulas and Concepts:
Algebra I
- Terms/Coefficients
- Expanding/Factoring
Pre-Calculus
Trigonometric Identities
- Product-to-Sum Formula:
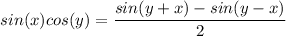
Calculus
Differentiation
- Derivatives
- Derivative Notation
Derivative Property [Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [cf(x)] = c \cdot f'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/s293bflxm18bvcg1l3en3cuunq0lisacx0.png)
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Integration
- Integrals
- [Indefinite Integrals] Integration Constant C
Integration Property [Multiplied Constant]:
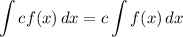
Integration Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle \int {[f(x) \pm g(x)]} \, dx = \int {f(x)} \, dx \pm \int {g(x)} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/college/vv6tmdt2ebyhbe4340gy3q8mh1dbk7tosc.png)
U-Substitution
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
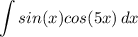
Step 2: Integrate Pt. 1
- [Integrand] Rewrite [Product-to-Sum Formula]:
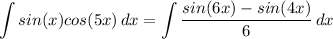
- [Integrand] Rewrite:
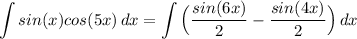
- [Integral] Rewrite [Integration Property - Addition/Subtraction]:
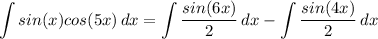
- [Integrals] Rewrite [Integration Property - Multiplied Constant]:
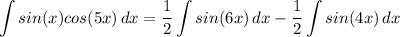
- Factor:
![\displaystyle \int {sin(x)cos(5x)} \, dx = (1)/(2) \bigg[ \int {sin(6x)} \, dx - \int {sin(4x)} \, dx \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/college/zqwtfqh04zc0xxtkb5bxpx2x7epc3a0lct.png)
Step 3: integrate Pt. 2
Identify variables for u-substitution.
Integral 1:
- Set u:
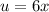
- [u] Differentiate [Basic Power Rule, Multiplied Constant]:
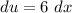
Integral 2:
- Set z:
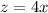
- [z] Differentiate [Basic Power Rule, Multiplied Constant]:
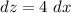
Step 4: Integrate Pt. 3
- [Integrals] Rewrite [Integration Property - Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle \int {sin(x)cos(5x)} \, dx = (1)/(2) \bigg[ (1)/(6)\int {6sin(6x)} \, dx - (1)/(4)\int {4sin(4x)} \, dx \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/college/tl5lelwwrzr6hna74kwwl104cd08ipx7fl.png)
- [Integrals] U-Substitution:
![\displaystyle \int {sin(x)cos(5x)} \, dx = (1)/(2) \bigg[ (1)/(6)\int {sin(u)} \, du - (1)/(4)\int {sin(z)} \, dz \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/college/f8c1x3awfi8abhruqdyzhnw9gjbgsggu1f.png)
- [Integrals] Trigonometric Integration:
![\displaystyle \int {sin(x)cos(5x)} \, dx = (1)/(2) \bigg[ (1)/(6)[-cos(u)] - (1)/(4)[-cos(z)] \bigg] + C](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/college/g94xsqwcowym25zihgu6mtvjzevqzdwpn7.png)
- Simplify:
![\displaystyle \int {sin(x)cos(5x)} \, dx = (1)/(2) \bigg[ (cos(z))/(4) - (cos(u))/(6) \bigg] + C](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/college/rrsh4bda7m09t8l47a1p099uc92csyemr9.png)
- Expand:
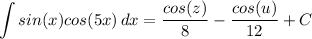
- Back-Substitute:
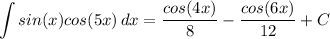
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Integration