Answer:
1- All of the elements, except for Hydrogen and Helium, originated from the life and death of a Star.
2- A Main Sequence Star (such as our sun) is in a state of equilibrium.
3- Temperature affects a star’s color. The hottest stars appear to be what color?
Blue
4- What determines the life cycle of a star?
The mass of the star.
5- There are billions of stars in the universe. How are they classified?
by their temperature and luminosity
Step-by-step explanation:
1) At the beginning of the universe there was only hydrogen and helium, since they were the most simple elements on their structure. Then, stars born from molecular clouds of hydrogen and helium and once they reach the necessary temperature on their core, they start the nucleosynthesis (the fuse of lighter element into heavier elements), for example, hydrogen into helium and helium into berilium.
2) In the stars, there is an equilibrium between two forces, the force of gravity in the inward direction due to their own mass and the radiation pressure in the upward direction as a consequence of the nuclear reaction in their core, that is known as hydrostatic equilibrium.
The radiation pressure is gotten from the nuclear reactions at the core (when lighter elements fuse in heavier elements), but if the nuclear reactions stop, hence, the radiation pressure will also do it and the force of gravity will overcome and break the equilibrium.
Main sequence star is in the state of fuse hydrogen into helium at its core, once the hydrogen is exhausted, the equilibrium breaks since there is not radiation pressure in the upward direction to counteract the force of gravity.
3) Bodies that are hot enough emit light as a consequence of their temperature. For example, an iron bar in contact with fire will start to change colors as the temperature increases, until it gets to a blue color, that is known as Wien's displacement law, which establishes that the peak of emission for the spectrum¹ will be displaced to shorter wavelengths as the temperature increases.
The same scenario described above can be found in the star. A star with high temperature will have a blue color and one with low temperature will have a red color.
4) The evolution of a star is determined exclusively by its mass. For example, a star with more than 8 solar masses will end up its life as a neutron star or a black hole. In the other hand, a star with less of 8 solar masses will end up its life as a planetary nebula or a white dwarf.
5) Stars can be classified by their temperature, since it is easy to determine it by means of their spectrum and Wien's displacement law:
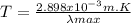
In the other hand, since stars do not have the same size, they have different brightness, since the free mean path of light will be greater in bigger radius.
Key term:
¹Spectrum: decomposition of light on its characteristic colors (wavelengths).