Answer:
-193.8 kJ is the heat of reaction
Step-by-step explanation:

Standard heat of formation of
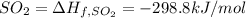
Standard heat of formation od
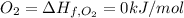
Standard heat of formation of
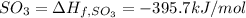
The heat of reaction =∑(Heat formation of products )-∑( heat of fromation of reactants)
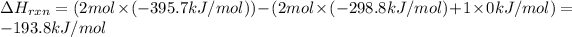
-193.8 kJ/mol is the heat of reaction