Answer : The molar mass (g/mole) of the compound is, 2707.55 g/mole
Solution : Given,
Mass of solute = 33.2 g
Volume of solution = 250 ml = 0.250 L
Temperature of solution =
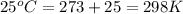
Formula used for osmotic pressure :
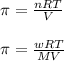
where,
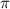 = osmotic pressure
= osmotic pressure
V = volume of solution
R = solution constant = 0.0821 L.atm/mole.K
T= temperature of solution
M = molar mass of solute
w = mass of solute
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get the molar mass of the compound.
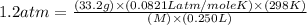
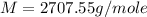
Therefore, the molar mass (g/mole) of the compound is, 2707.55 g/mole