Answer:
1.
Step-by-step explanation:
1.
The STP conditions refer to the standard temperature and pressure. Pressure values at 1 atmosphere and temperature at 0 ° C are used and are reference values for gases. And in these conditions 1 mole of any gas occupies an approximate volume of 22.4 liters.
To solve this case, you must first know how many moles represent 45 L of H2S. For that you apply a simple rule of three: if 1 mole of H2S occupies a volume of 22.4 L (by STP conditions), how many moles are there in 45 L?
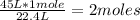 approximately
approximately
By stoichiometry of the reaction (that is, the relationship between the amount of reagents and products in a chemical reaction), you know that 2 moles of H2S react with 3 moles of O2. So, for 45 L of H2S (2 moles) to react, 3 moles of O2 is necessary. To calculate the volume that these 3 moles represent, you use again a rule of three in STP conditions: if 1 mole occupies 22.4 L, how much volume does 3 moles occupy?
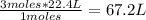
This means that 67.2 L of O2 are needed to react completely with 45.0 L of H2S at STP
2.
The main quantum number (n) describes the size of the orbital.
The magnetic quantum number (ml) determines the spatial orientation of the orbital. It is called magnetic because this spatial orientation is usually defined in relation to an external magnetic field.
The quantum number of the angular orbital moment (l) describes the shape of the atomic orbital.
The orbitals s (l = 0) have a spherical shape. The extent of this orbital depends on the value of the main quantum number.
The orbitals p (l = 1) are formed by two identical lobes that project along an axis. The junction zone of both lobes coincides with the atomic nucleus. There are three orbitals p (m = -1, m = 0 and m = + 1) in the same way, which differ only in their orientation along the axes.
The orbitals d (l = 2) are also formed by lobes. There are five types of d orbitals (corresponding to m = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2).
The orbitals f (l = 3) have a multilobular aspect (several lobes) distributed in the axes. There are seven types of orbitals f (corresponding to m = -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3).
The relative energies between the sub-levels are s <p <d <f. And two factors control the energy of an orbital: its size and shape. A larger size and more complex shape, requires more energy.
3.
An ionic bond is produced between metallic and non-metallic atoms, where electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another. During this process, one atom loses electrons and another one gains them, forming ions. Usually, the metal gives up its electrons forming a cation to the nonmetal element, which forms an anion.
Lithium fluoride is a chemical compound formed through this chemical bond of formula LiF. The electronic configuration of Li is
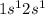 and that of fluorine is
and that of fluorine is
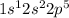 . When these atoms come into contact, the 2s1 valence electron of the lithium is transferred to the F atom.
. When these atoms come into contact, the 2s1 valence electron of the lithium is transferred to the F atom.