Answer:
We have the function:
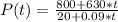
a) The population of deer when t = 60 is equal to P(60)
We just need to replace t by 60 in the above equation:
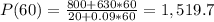
We can not have the 0.7 of a deer, so we could round this up to 1,520
So at t = 60, we would have around 1,520 deers.
b) The horizontal asymptote of P(t) = y is when the denominator of the function is equal to zero (this is when P(t) goes to infinity).
Then we need to find the value of t such that:
20 + 0.09*t = 0
20 = -0.09*t
20/-0.09 = t = -222.222...
The asymptote of P(t) is at t = -222.222...
Because in this case t is negative, the function will diverge to infinity and minus infinity.
c) We can ignore the asymptotes and only compute this for positive values of t.
To find the maximum, we first need to look at the zeros of the first derivative of P(t):
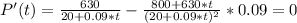
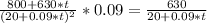
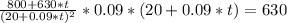
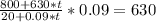
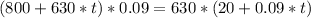
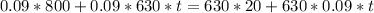
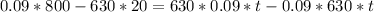
That last equation has no real solution, this means that we do not have a maximum. Then we will have a vertical asymptote
Then we can just look at the graph of the function (is below)
And you can see that we have a horizontal asymptote at y = 7000, then this will be the maximum number of deers.