Answer: -550.059 J
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the amount of work done for an isothermal process is given by the equation:
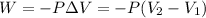
W = amount of work done = ?
P = pressure = 1.00 atm
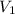 = initial volume = 1.00 L
= initial volume = 1.00 L
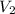 = final volume = 6.43 L
= final volume = 6.43 L
Putting values in above equation, we get:
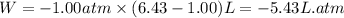
To convert this into joules, we use the conversion factor:
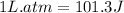
So,
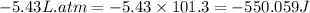
The negative sign indicates the system is doing work.
Hence, the work done on the surroundings is -550.059 J