Answer: 1) Second option is correct.
2) First option is correct.
Explanation:
Since we have given that
Total number of cards drawn = 16
Number of the cards are spades = 5
The experimental probability of drawing a spade is given by
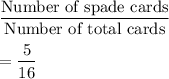
Hence, Second option is correct.
As we know that total number of cards in a deck = 52
Number of spades in a deck = 13
So, Theoretical probability of getting a spade is given by
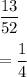
so, the difference between the theoretical and experimental probability is
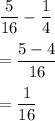
Hence, First option is correct.