The solubility of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) in water at
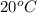
is 0.02335
mol/L. When a Ca(OH)2 solution has a concentration of 0.02335 mol/L at the said temperature, a saturated solution is formed.
Upon dissolution and dissociation of 1 mole Ca(OH)2, 1 mole of calcium ion (
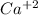 ) and 2 moles of hydroxide ions (
) and 2 moles of hydroxide ions (
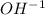 ) are formed. The concentration of the hydroxide ions determine the pH of the solution. This same concentration would be needed in calculating the concentration of lye solution needed.
) are formed. The concentration of the hydroxide ions determine the pH of the solution. This same concentration would be needed in calculating the concentration of lye solution needed.
1. To calculate the pH of the solution, a few approaches are possible. Here, the pOH of the solution is calculated first using the molar concentration of
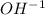 ions. Because pH + pOH = 14, the pH of the solution can then be calculated by subtracting pOH from 14.
ions. Because pH + pOH = 14, the pH of the solution can then be calculated by subtracting pOH from 14.
Because 2 moles of
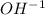 ions are formed per mole of Ca(OH)2 dissolved, the pOH of a saturated Ca(OH)2 solution at
ions are formed per mole of Ca(OH)2 dissolved, the pOH of a saturated Ca(OH)2 solution at
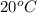 is,
is,
*Concentration (
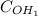 ) of
) of
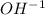 ions,
ions,
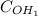 = 0.02335 mol Ca(OH)2/L * 2 mol
= 0.02335 mol Ca(OH)2/L * 2 mol
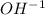 / 1 mol Ca(OH)2
/ 1 mol Ca(OH)2
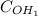 = 0.0467 mol
= 0.0467 mol
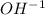 /L
/L
*pOH of saturated Ca(OH)2 solution,
pOH = -log [
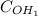 ]
]
pOH = -log [0.0467 mol
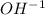 /L ]
/L ]
pOH = 1.33
*pH of saturated Ca(OH)2 solution,
pH = 14 - 1.33
pH = 12.67
2. To find the concentration of lye (NaOH) solution that would give the same pH as a saturated Ca(OH)2 solution at the same temperature, the pOH of the saturated Ca(OH)2 solution will be used.
For every mole of NaOH that dissolves and dissociates, 1 mole of
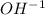 ions is formed. Thus,
ions is formed. Thus,
*Concentration (
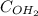 ) of
) of
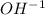 ions,
ions,
pOH = -log [
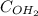 ]
]
1.33 = -log [
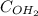 ]
]
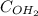 = 10^-1.33
= 10^-1.33
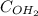 = 0.0467 mol
= 0.0467 mol
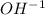 / L
/ L
Because 1 mole of NaOH produces only 1 mole of
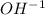 ions, the concentration of the
ions, the concentration of the
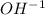 ions should then be equal to the concentration of the lye (NaOH) solution. Thus, 0.0467 mol/L of lye would give the same pH as that of 0.0233 mol/L (saturated) Ca(OH)2 solution at
ions should then be equal to the concentration of the lye (NaOH) solution. Thus, 0.0467 mol/L of lye would give the same pH as that of 0.0233 mol/L (saturated) Ca(OH)2 solution at
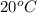 . The pH of both solutions is 12.67.
. The pH of both solutions is 12.67.