we know that
the formula to calculate the distance between two points is equal to
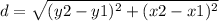
In this problem we have
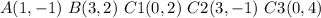
Step 1
Find the distance AB
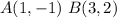
Substitute the values in the formula
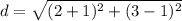
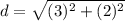
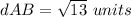
Step 2
Find the distance AC1
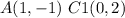
Substitute the values in the formula
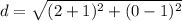
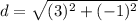
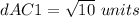
Step 3
Find the distance BC1
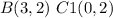
Substitute the values in the formula
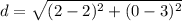
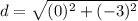
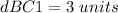
Step 4
Find the distance AC2
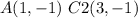
Substitute the values in the formula
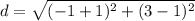
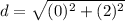
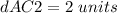
Step 5
Find the distance BC2

Substitute the values in the formula
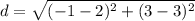
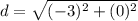
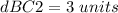
Step 6
Find the distance AC3
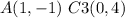
Substitute the values in the formula
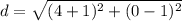

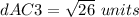
Step 7
Find the distance BC3
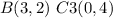
Substitute the values in the formula
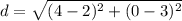
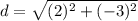
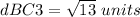
we know that
If the length sides of the triangle satisfy the Pythagoras Theorem. then the triangle is a right triangle
The formula of the Pythagoras Theorem is equal to
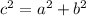
where
c is the hypotenuse (the greater side)
a and b are the legs of the triangle
Step 8
Verify if the triangle ABC1 is a right triangle
we have
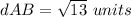
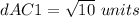
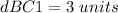
Applying Pythagoras theorem
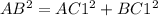
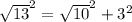
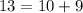
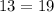 --------> is not true
--------> is not true
therefore
the triangle ABC1 is not a right triangle
Step 9
Verify if the triangle ABC2 is a right triangle
we have
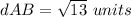
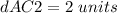
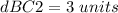
Applying Pythagoras theorem
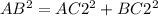
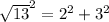
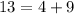
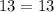 --------> is true
--------> is true
therefore
the triangle ABC2 is a right triangle
Step 10
Verify if the triangle ABC3 is a right triangle
we have
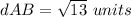
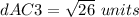
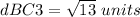
Applying Pythagoras theorem
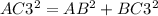
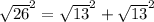
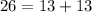
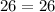 --------> is true
--------> is true
therefore
the triangle ABC3 is a right triangle
therefore
the answer is
