Step 1
Plot the vertices of triangle PQR
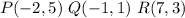
using a graphing tool
see the attached figure
we know that the distance between two points is equal to
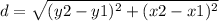
Step 2
Find the distance PR
substitute the values
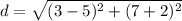
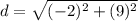
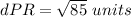
Step 3
Find the distance QP
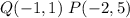
substitute the values
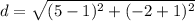
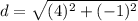
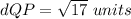
Step 4
Find the distance QR
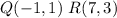
substitute the values
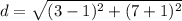
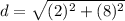
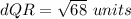
Step 5
If triang;le PQR is a right triangle
then
Applying the Pythagorean Theorem
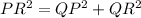
substitute the values
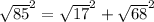
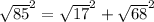
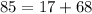
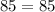 ---------> is true
---------> is true
therefore
The answer is
The triangle PQR is a right triangle