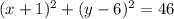case A)
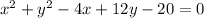
Convert to standard form
Group terms that contain the same variable, and move the constant to the opposite side of the equation
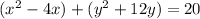
Complete the square twice. Remember to balance the equation by adding the same constants to each side.
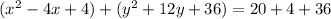
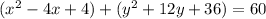
Rewrite as perfect squares
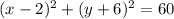
therefore
the answer case A) is
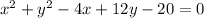 ----->
----->
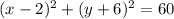
case B)
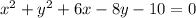
Convert to standard form
Group terms that contain the same variable, and move the constant to the opposite side of the equation
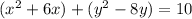
Complete the square twice. Remember to balance the equation by adding the same constants to each side.
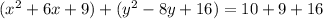
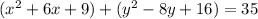
Rewrite as perfect squares
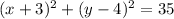
therefore
the answer case B) is
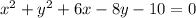 ----->
----->
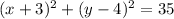
case C)
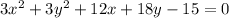
Convert to standard form
Group terms that contain the same variable, and move the constant to the opposite side of the equation
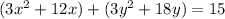
Factor the leading coefficient of each expression
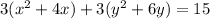
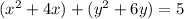
Complete the square twice. Remember to balance the equation by adding the same constants to each side.
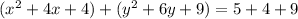
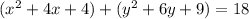
Rewrite as perfect squares
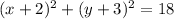
therefore
the answer case C) is
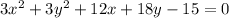 ----->
----->
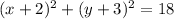
case D)
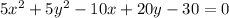
Convert to standard form
Group terms that contain the same variable, and move the constant to the opposite side of the equation
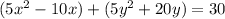
Factor the leading coefficient of each expression
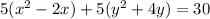
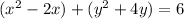
Complete the square twice. Remember to balance the equation by adding the same constants to each side.
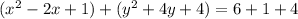
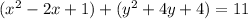
Rewrite as perfect squares
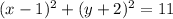
therefore
the answer case D) is
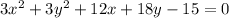 ----->
----->
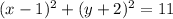
case E)
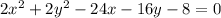
Convert to standard form
Group terms that contain the same variable, and move the constant to the opposite side of the equation
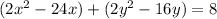
Factor the leading coefficient of each expression
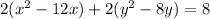
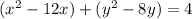
Complete the square twice. Remember to balance the equation by adding the same constants to each side.
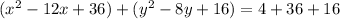
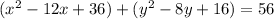
Rewrite as perfect squares
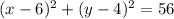
therefore
the answer case E) is
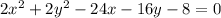 ----->
----->
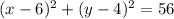
case F)
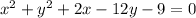
Convert to standard form
Group terms that contain the same variable, and move the constant to the opposite side of the equation
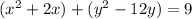
Complete the square twice. Remember to balance the equation by adding the same constants to each side.
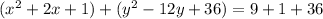
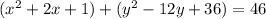
Rewrite as perfect squares
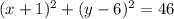
therefore
the answer case F) is
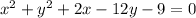 ----->
----->