ANSWERx = 5/4
Step-by-step explanation 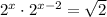
Note that
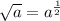
so
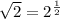
Note that on the left-hand side, we can use exponent properties for multiplying two powers of the same base together:
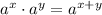
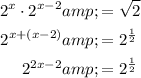
We can now equate the exponents because both sides of the equation are of the same base with no other terms.
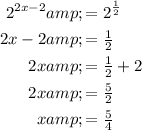
The answer is x = 5/4. We can confirm this by using this value in the original equation to get a true statement.