Balanced chemical equation of potassium chlorate heated to form potassium chloride and oxygen:
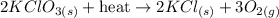
Reaction type: Decomposition reaction.
Now we will use the stoichiometry to calculate the masses of reactants and products after reaction completion.
We are given that the mass of KClO3 = 5.00x10^15 ng = 5000000 g
We will first calculate the number of moles of KClO3 and use the stoichiometry to calculate other masses.
number of moles (n) of KClO3:
n = m/M where m is the mass in grams and M is the molar mass in g/mol
n = (5000000 g)/(122,55g/mol)
n = 40799.67 mol of KClO3
Mass of KCl:
To find the number of moles of KCl, we will use the molar ratio between KClO3:KCl which is 2:2 according to the equation. Therefore number of moles of KCl = 40799.67 mol
m = nM
m = (40799.67 mol) x (74,5513 g/mol)
m = 3041668.707 g
Mass of Oxygen:
We will use the molar ratio between KClO3:O2 which is 2:3, therefore the number of moles of O2 = 40799.67 x (3/2) = 61199.505 mol
m = nM
m = (61199.505 mol) x (15.999 x 2)
m = 1958261.761 g
There should be NO mass of KClO3 after the reaction.
However, initially we had a mass of 5000000 g of KClO3 before the reaction. After the reaction a mass of 3041668.707 g KCl and 1958261.761 g O2 was produced whuch in total is = 4999930.468 g
The mass of KClO3 left = 5000000 g - 4999930.468 g = 69.532 g