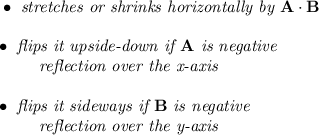

that said, let's say then, we have f(x)
2f(x), will make A = 2, and therefore, will "shrink" the graph vertically by a factor of twice as much from f(x).
f(-x) or f(-1x) will make B = -1, therefore, will simply flip the graph over the y-axis, rotation over the y-axis, just a mirror image.
f(x) - 1 will make D = -1, that means, a downward vertical shift of 1 unit, so the graph will drop by 1.
2f(-x) -1, shrunk by twice, mirror over the y-axis, and dropped by 1.