Answer:
1) Average velocity = 10/3 m/s
2) Instantaneous velocity = -2 m/s
Speed = 2 m/s to the left
3) (0, 3) ∪ (6, 8]
4) Going faster: (3, 4.5) ∪ (6, 8]
Slowing down: (0, 3) ∪ (4.5, 6)
5) Total distance = 35.67 m (nearest hundredth)
Explanation:
The relationships between position (displacement), velocity and acceleration are:

Given a particle is moving with velocity v(t) = t² - 9t + 18, to find its position s(t) we can integrate v(t):
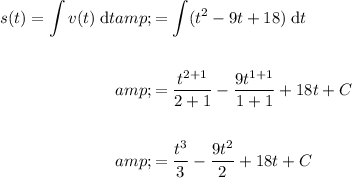
As s(0) = 1, then:

Therefore, the position function s(t) is:

Given a particle is moving with velocity v(t) = t² - 9t + 18, to find its acceleration a(t) we can differentiate v(t):
![\begin{aligned}a(t)=\frac{\text{d}}{\text{d}t}[v(t)]&=2\cdot t^(2-1)-1\cdot9t^(1-1)+0\\&=2t-9\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/tgzefb9v0rcfi175trl5wvt7rh64l2dglk.png)
Therefore, the acceleration function a(t) is:


Question 1
To find the average velocity over the interval [0, 8], use the formula:

In this case:
Calculate the position at t₁ and t₂ by substituting t = 0 and t = 8 into s(t):


Therefore:

Therefore, the average velocity is 10/3 m/s.

Question 2
To find the instantaneous velocity at t = 5 seconds, substitute t = 5 into v(t):

So, the instantaneous velocity at t = 5 seconds is -2 m/s.
Speed is a scalar quantity that measures how fast an object is moving regardless of its direction. Therefore, speed is the magnitude of velocity:

Therefore, the speed at t = 5 is 2 m/s to the left.

Question 2
The particle changes direction when v(t) = 0.

Therefore, the particle changes direction at t = 3 and t = 6.
We know that the position of the particle at t = 0 is 1 meter right of zero. Therefore:
- It is moving to the right in the interval (0, 3).
- It is moving to the left in the interval (3, 6).
- It is moving to the right in the interval (6, 8].
Therefore, the time intervals between 0 ≤ t ≤ 8 when the particle is moving right is:

Question 4
When a(t) > 0:

When a(t) < 0:

Therefore:
- Velocity is positive in the interval (0, 3) and (6, 8].
- Velocity is negative in the interval (3, 6).
- Acceleration is positive in the interval (4.5, 8].
- Acceleration is negative in the interval (0, 4.5).
(Refer to the attachment).
If velocity and acceleration have the same sign, it means the object is speeding up.
If velocity and acceleration have opposite signs, it means the object is slowing down.
Therefore, the time intervals when the particle is going faster and slowing down are:
- Going faster: (3, 4.5) ∪ (6, 8]
- Slowing down: (0, 3) ∪ (4.5, 6)

Question 5
To find the total distance the particle has traveled between 0 and 8 seconds, we need to consider the distance traveled between the intervals when it changes direction.
To do this, find the position of the particle at t = 0, t = 3, t = 6 and t = 8.




Therefore, in the interval 0 ≤ t < 3, the particle travels:

In the interval 3 < t < 6, it travels:

In the interval 6 < t ≤ 8, it travels:

So the total distance the particle has traveled between 0 and 8 seconds is:
