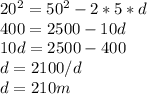Answer:
the train travels 210 m
Step-by-step explanation:
Kinematics equations of motion
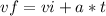 , equation(1)
, equation(1)
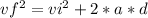 equation(2)
equation(2)
Vi= initial velocity (m/s)
Vf= final velocity (m/s)
a = acceleration
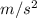
d= traveling distance (m)
known information:
vi=50m/s
a=-5
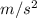
t=6 s
Calculation of the final speed replacing the information known in the equation 1
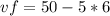
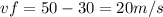
Calculation of the distance replacing the information known and the final velocity in the equation 2