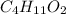Find grams of C and H, using molar masses:
12.0 g C x (1.900 g CO2 / 44.0 g CO2) = 0.5182 grams C
2.02 g H x (1.070 g H2O /18 g H2O) = 0.1201 grams H
Since all the C and H in CO2 and H2O will come from the sample except oxygen, because we need to provide oxygen for sample to burn.
0.9835 g sample - 0.5182 g O - 0.1201 g H = 0.3452 grams O
find moles, using molar masses:
0.5182 grams C / 12.0 g/mol C = 0.0432 moles C
0.1201 grams H / 1.01 g/mol H = 0.119 moles H
0.3452 grams O / 16.0 g/mol O = 0.0216 moles O
0.0216 is lesser, so use it to normalize to find the ratio.
find ratios:
0.0432 moles C / 0.0216 = 2 moles C
0.119 moles H / 0.0216 = 5.5 moles H
0.0216 moles O / 0.0216 = 1 mole O
so, the ratio is C2 H{5.5} O1
double the ration to eliminate decimals.
gives your answer is