Answer:
2.264 (3 d.p.)
Explanation:
Given integral:
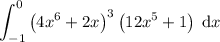
First, evaluate the indefinite integral using the method of substitution.
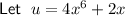
Find du/dx and rewrite it so that dx is on its own:
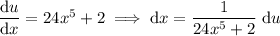
Rewrite the original integral in terms of u and du, and evaluate:
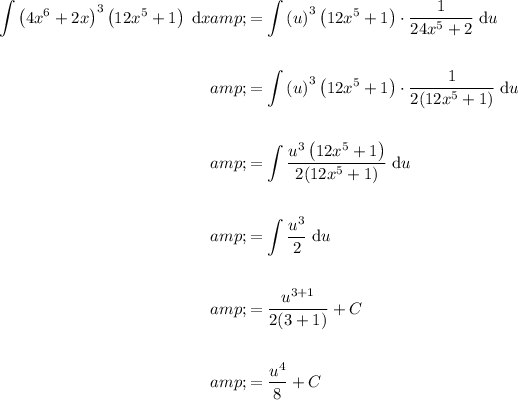
Substitute back u = 4x⁶ + 2x:
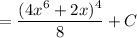
Therefore:
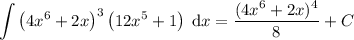
To evaluate the definite integral, we must first determine any intervals within the given interval -1 ≤ x ≤ 0 where the curve lies below the x-axis. This is because when we integrate a function that lies below the x-axis, it will give a negative area value.
Find the x-intercepts by setting the function to zero and solving for x.
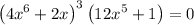
Therefore:
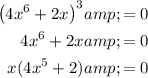
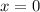
![\begin{aligned}4x^5+2&=0\\4x^5&=-2\\x^5&=-(1)/(2)\\x&=\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(2)}\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/2636vuzn73eti5w1j2vqn7ymvlk3xd4slk.png)
![\begin{aligned}12x^5+1&=0\\12x^5&=-1\\x^5&=-(1)/(12)\\x&=\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(12)}\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/s0s2yns6jqpkb27ttog5sf8yaekc1h0i1o.png)
Therefore, the curve of the function is:
- Below the x-axis between -1 and ⁵√(-1/2).
- Above the x-axis between ⁵√(-1/2) and ⁵√(-1/12).
- Below the x-axis between ⁵√(-1/12) and 0.
So to calculate the total area, we need to calculate the positive and negative areas separately and then add them together, remembering that if you integrate a function to find an area that lies below the x-axis, it will give a negative value.
Integrate the function between -1 and ⁵√(-1/2).
As the area is below the x-axis, we need to negate the integral so that the resulting area is positive:
![\begin{aligned}A_1&=-\displaystyle \int_(-1)^{\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(2)}} \left(4x^6+2x\right)^3\left(12x^5+1\right)\;\text{d}x\\\\&=-\left[((4x^6+2x)^4)/(8)\right]_(-1)^{\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(2)}}\\\\&=-\left[\left(\frac{\left(4\left(\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(2)}\right)^6+2\left(\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(2)}\right)\right)^4}{8}\right)-\left(((4(-1)^6+2(-1))^4)/(8)\right)\right]\\\\&=-[0-2]\\\\&=2\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/lpqkw7pwuu4x2q3vrhtsbpxmmgmakiqy78.png)
Integrate the function between ⁵√(-1/2) and ⁵√(-1/12).
![\begin{aligned}A_2&=\displaystyle \int_{\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(2)}} ^{\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(12)}} \left(4x^6+2x\right)^3\left(12x^5+1\right)\;\text{d}x\\\\&=\left[((4x^6+2x)^4)/(8)\right]_{\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(2)}}^{\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(12)}}\\\\&=\left(\frac{\left(4\left(\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(12)}\right)^6+2\left(\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(12)}\right)\right)^4}{8}\right)-\left(\frac{\left(4\left(\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(2)}\right)^6+2\left(\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(2)}\right)\right)^4}{8}\right)\\\\\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/f40pvphg4xxn7zlbkyzfl6jnws39ii8qek.png)
![\begin{aligned}&=\frac{625}{648\sqrt[5]{12^4}}-0\\\\&=0.132117398...\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/2ts2d8tkpg6qpgnxf89ty6evbb0r4a3455.png)
Integrate the function between ⁵√(-1/12) and 0.
As the area is below the x-axis, we need to negate the integral so that the resulting area is positive:
![\begin{aligned}A_3&=-\displaystyle \int_{\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(12)}}^0 \left(4x^6+2x\right)^3\left(12x^5+1\right)\;\text{d}x\\\\&=-\left[((4x^6+2x)^4)/(8)\right]_{\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(12)}}^0\\\\&=-\left[\left(((4(0)^6+2(0))^4)/(8)\right)-\left(\frac{\left(4\left(\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(12)}\right)^6+2\left(\sqrt[5]{-(1)/(12)}\right)\right)^4}{8}\right)\right]\\\\&=-\left[0-\frac{625}{648\sqrt[5]{12^4}}\right]\\\\&=\frac{625}{648\sqrt[5]{12^4}}\\\\&=0.132117398...\\\\\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/5al0fi57arpjtcfsryujdkxla42pzfowk7.png)
To evaluate the definite integral, sum A₁, A₂ and A₃:
![\begin{aligned}\displaystyle \int^0_(-1) \left(4x^6+2x\right)^3\left(12x^5+1\right)\;\text{d}x&=2+2\left( \frac{625}{648\sqrt[5]{12^4}}\right)\\\\&=2+ \frac{625}{324\sqrt[5]{12^4}}\right}\\\\&=2.264\; \sf (3\;d.p.)\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/g4ro4wdnv5yn0eybdpo5hx0t1ow4jzizkj.png)