Specific heat equation is given as
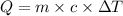
where, Q = energy required
m = mass
c = specific heat
 = change in temperature
= change in temperature
Specific heat of silver (
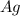 ) is
) is
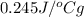
Mass of silver = 350 g
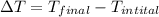
Convert 400 K to degree Celsius = 400-273 = 127 K
Convert 293 K to degree Celsius = 293-273 = 20 K
Thus,
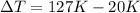
=
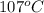
Put the values,
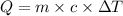
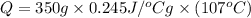
= 9175.25 J
Hence, energy required to raise the temperature is 9175.25 J