Given that the College Board reported the following mean scores for the three parts of the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT) ( The World Almanac , 2009):
Critical Reading 502
Mathematics 515
Writing 494
Assume that the population standard deviation on each part of the test is σ =
100.
We find the probability that a sample of 90 test takers will provide a sample mean test score within 10 points of the population mean of 502 on the critical reading part of the test (to 4 decimals) as follows:
Within 10 points of 502 implies (502 - 10, 502 + 10) = (492, 512).
Because the sample is large, we assume normal distribution.
The probability that the mean statistic of sample data is between two points (a, b) is given by:
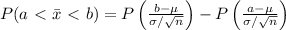
Thus,
![P(492\ \textless \ \bar{x}\ \textless \ 512)=P\left( (512-502)/(100/√(90)) \right)-P\left( (492-512)/(100/√(90)) \right) \\ \\ = P\left((10)/(10.5409) \right)-P\left((-10)/(10.5409) \right)=P(0.9487)-P(-0.9487) \\ \\ =P(0.9487)-[1-P(0.9487)]=2P(0.9487)-1=2(0.82861)-1 \\ \\ =1.65722-1=0.65722](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/college/q6kuco55llj6vmyn3781rh9s4dk6c3txh8.png)
Therefore, the probability that a sample of 90 test takers will provide a sample mean test score within 10 points of the population mean of 502 on the critical reading part of the test (to 4 decimals) is 0.6572.