Given the formula:
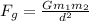
Where:
G = 6.67 x 10^-11
m1 = Mass of object per person
m2 - mass of earth
d = distance between objects
Let's solve for the gravitational forces.
We have:
1) Person at sea level:
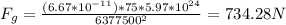
2) Person at peak of mount everest:
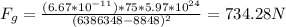
3) Tiangong-1 satellite:
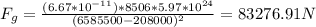
4) Space-X starlink satellite:
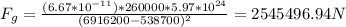
5) GPS satellites:
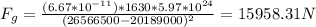
6) GOES weather satellite:
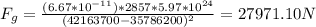
7) DirecTV satellite:
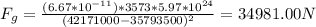
8) SiriusXM:
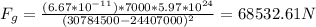
9) Moon:
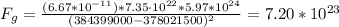
Part 2:
A satellite stay in orbit due to force of gravity and the statellites momentum from its launch into space.
A statellite may fall back to earth due to a drag that causes the staellites orbit go decay. This drag happens when the staellite run into traces of the earth's atmosphere.