Answer:
The balanced equation is
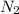 (g) + 3
(g) + 3
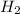 (g) ⇒ 2
(g) ⇒ 2
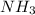 (g)
(g)
The coefficient in front of ammonia,
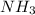 , in the balanced equation is 2.
, in the balanced equation is 2.
Step-by-step explanation:
The law of conservation of matter states that since no atom can be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, the number of atoms that are present in the reagents has to be equal to the number of atoms present in the products.
Then, you must balance the chemical equation. For that, you must first look at the subscripts next to each atom to find the number of atoms in the equation. If the same atom appears in more than one molecule, you must add its amounts
- Left side: 2 nitrogen and 2 hydrogen.
- Right side: 1 nitrogen and 3 hydrogen.
The coefficients located in front of each molecule indicate the amount of each molecule for the reaction. This coefficient can be modified to balance the equation, just as you should never alter the subscripts.
In this case you can start balancing the hydrogen. On the left side there is an amount of two hydrogens, while on the right side there are three. In order to match the amount of hydrogen on both sides, the easiest way to do this is by exchanging these numbers and adding them as coefficients in front of each molecule. It is as follows:
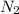 (g) + 3
(g) + 3
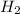 (g) ⇒ 2
(g) ⇒ 2
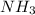 (g)
(g)
By multiplying the coefficient mentioned by the subscript, you get the amount of each element present in the reaction. So now you can calculate again the amount of elements on each side of the chemical reaction:
- Left side: 2 nitrogen and 6 hydrogen.
- Right side: 2 nitrogen and 6 hydrogen.
You can see that you have the same amount of each element on each side of the chemical equation. This indicates that the equation is balanced.
And the coefficient in front of ammonia,
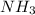 , in the balanced equation is 2.
, in the balanced equation is 2.