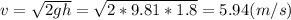We apply the simple principle of energy conservation. At height
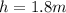
the pear has potential energy (and no kinetic energy). When it hits the ground the pear has kinetic energy (and no potential energy). Because the pear falls in a conservative force field (the gravitational field) the initial potential energy = final kinetic energy.
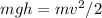
Thus its kinetic energy is
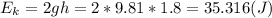
and its speed is