Answer:
ΔV=V1-V2 = 27692307.69volts
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello! Let's solve this!
The formula to calculate the power difference is
ΔV=V1-V2
V = k * (q / r)
k is a constant that equals
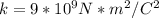
The data we have are:
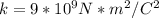
r = 0.0013m
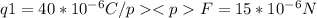
From the following formula we can calculate how much q2 is
F = k * (q1 * q2 / r2)
q2 = (F * r2) / (k * q1)
q2 = (15*10^{-6} N[/tex] * 0.00132) / (9*10^{9}N*m^{2}/C^{2}[/tex] *40*10^{-6}C\)
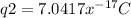
Now we calculate with q1 and q2, V1 and V2 respectively.
V1 = (9*10^{9}N*m^{2}/C^{2}[/tex] * 40*10^{-6}C\) /0.0013m
V1 = 27692307.69 volts
V2 = (9*10^{9}N*m^{2}/C^{2}[/tex] * 7.0417x^{-17}C[/tex]) /0.0013m
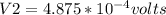
Then we solve the potential difference:
V1-V2 = 27692307.69 volts-4.875*10^{-4}volts[/tex]
ΔV=V1-V2 = 27692307.69volts