Answer:
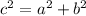
Explanation:
The legs of a right angle triangle measure 'a' and 'b'
Hypotenuse of the triangle measures 'c'
Pythagorean theorem states that square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of each leg
sum of the squares of each leg is
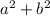
This is equal to the square of the hypotenuse c^2
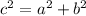 is the Pythagorean theorem
is the Pythagorean theorem