The net work done on the box weighing 5.0 kg and accelerated from rest by a force across a floor is 490 Nm.
Given the following data:
- Initial velocity = 0 m/s (since the box starts from rest).
- Acceleration = 2
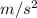
To find the net work done on the box:
First of all, we would determine the force acting on the box:
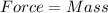 ×
×
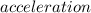
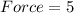 ×
×
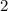
Force = 10 Newton
Next, we would use the second equation of motion to determine the distance traveled by the box:
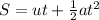
Where:
- S is the displacement or distance traveled.
- u is the initial velocity.
- t is the time measured in seconds.
Substituting the given parameters into the formula, we have;
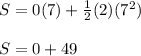
Distance, S = 49 meters.
Now, we can determine the net work done on the box:
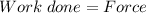 ×
×
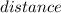
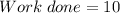 ×
×
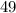
Work done = 490 Nm
Therefore, the net work done on the box is 490 Nm.