Answer : The moles of oxygen present in the sample is, 0.2 moles
Explanation : Given,
Moles of carbon = 0.200 mole
Moles of hydrogen = 0.400 mole
Mass of unknown compound = 6.00 g
Molar mass of carbon = 12 g/mole
Molar mass of hydrogen = 1 g/mole
Molar mass of oxygen = 16 g/mole
First we have to calculate the mass of carbon and hydrogen.
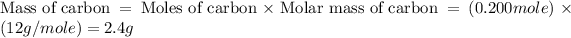
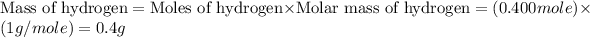
Now we have to calculate the mass of oxygen.
Total mass of unknown compound = Mass of carbon + Mass of hydrogen + Mass of oxygen
6.00 = 2.4 + 0.4 + Mass of oxygen
Mass of oxygen = 3.2 grams
Now we have tom calculate the moles of oxygen.
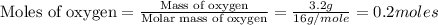
Therefore, the moles of oxygen present in the sample is, 0.2 moles