We are presented with a reaction that takes place in the gas phase, both reactants and products are in the form of gas. We will apply the ideal gas law to solve the problem. We have the following equation:
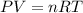
where,
P=Pressure=300kPa = 2.96077atm
V of HCN=116 L
T= 1200°C =1473.15K
R= Ideal gas constant = 0.08206 (amt L)/(mol K)
n= Number of moles of HCN
We can find the number of moles of HCN using the ideal gas law. We clear n from the equation:
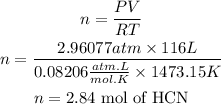
With this information, we can find the moles of water vapor formed. If we look at the reaction, for every 2 moles of HCN formed, 6 moles of water are formed, the ratio is 1 to 3. So, we must multiply the number of moles of HCN by 3.
Number of moles of water = Number of moles of HCN x 3= 2.84 x 3= 8.52 mol of H2O.
Now we will apply the ideal gas equation again but now we will clear the volume. We will assume that the temperature and pressure remain constant. We have:
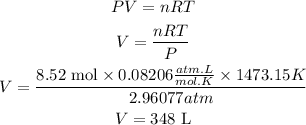
So, the volume of water vapour produced is 348L